1. Introduction
Purpose and scope
This runbook explains how a backend service or component can integrate with the Verifier as an Authorization Server (AS) in M2M mode. It provides the end-to-end steps needed by developers: from preparing configuration and credentials, to calling the Token Endpoint with a LEARCredentialMachine, to using access tokens to consume protected APIs.
-
Integration of backend services with the Verifier using M2M authentication.
-
Use of LEARCredential inside a Verifiable Presentation (VP) as the client assertion.
-
OAuth 2.1 client_credentials profile with Private Key JWT.
-
Token acquisition and usage for accessing Verifier-protected resources.
-
Security, error handling, observability.
Intended audience
-
Developers building components/services in the ecosystem.
-
Technical integrators responsible for connecting a system to the Verifier.
-
SRE and security engineers validating compliance.
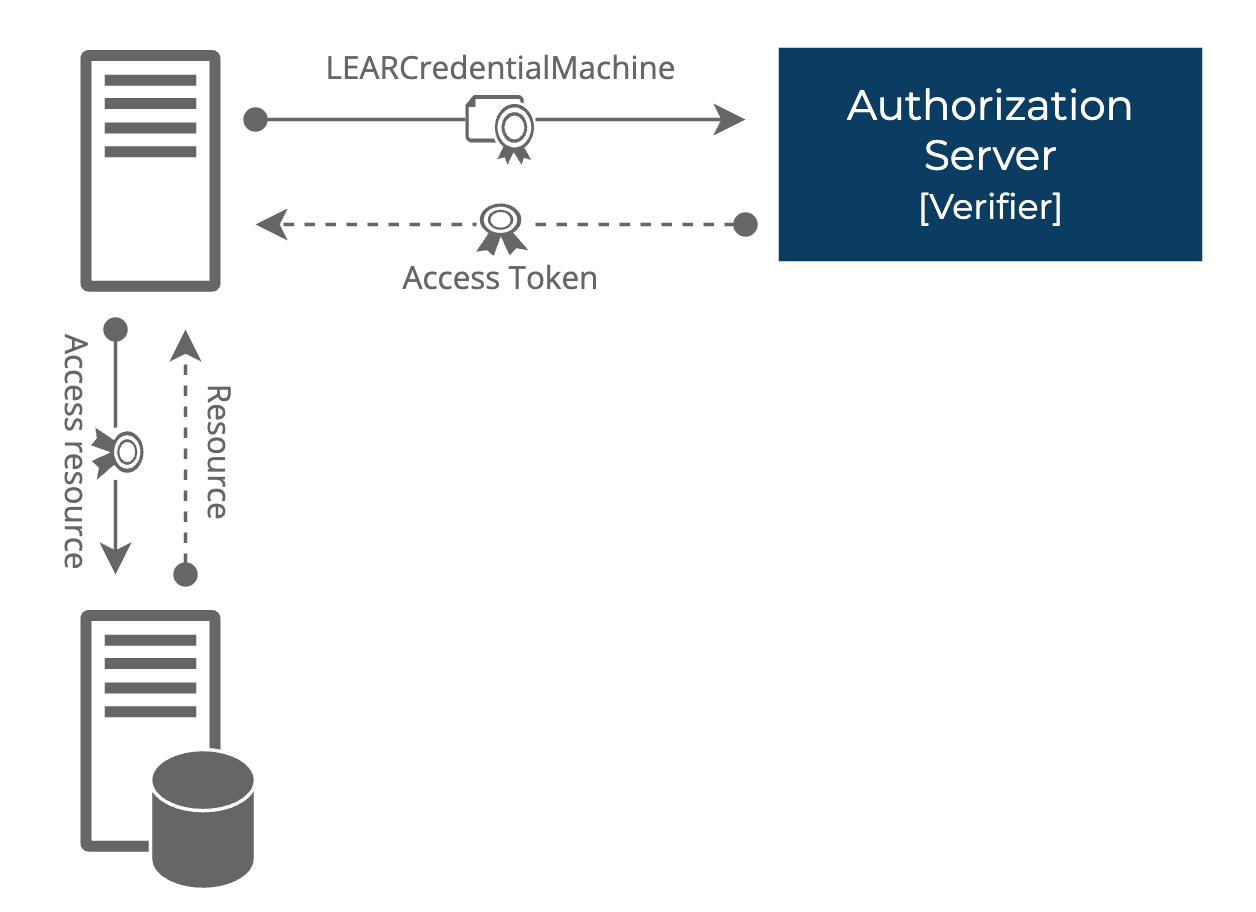
High‑level architecture
-
Client requests access token from Verifier Token Endpoint using client_credentials grant and client_assertion = VP (containing LEARCredentialMachine).
-
Verifier authenticates client, validates VP and LEARCredentialMachine.
-
Verifier issues access token with 1h lifetime.
-
Client uses access token to call protected resources.
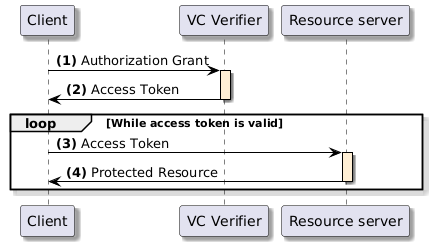
High-level flow
-
The client requests an access token by authenticating with the authorization server (VCVerifier) and presenting the authorization grant. Since the client authentication is used as the authorization grant, no previous authorization request is needed.
-
The authorization server authenticates the client and validates the authorization grant, and if valid, issues an access token.
-
The client requests the protected resource from the resource server and authenticates by presenting the access token.
-
The resource server validates the access token presented and if valid, returns the resource requested.

No Comments